The ELF linker transitioned away from archive indexes in
https://reviews.llvm.org/D117284.
This paves the way for supporting `--start-lib`/`--end-lib` (See #77960)
The ELF linker unified library handling with `--start-lib`/`--end-lib` and removed
the ArchiveFile class in https://reviews.llvm.org/D119074.
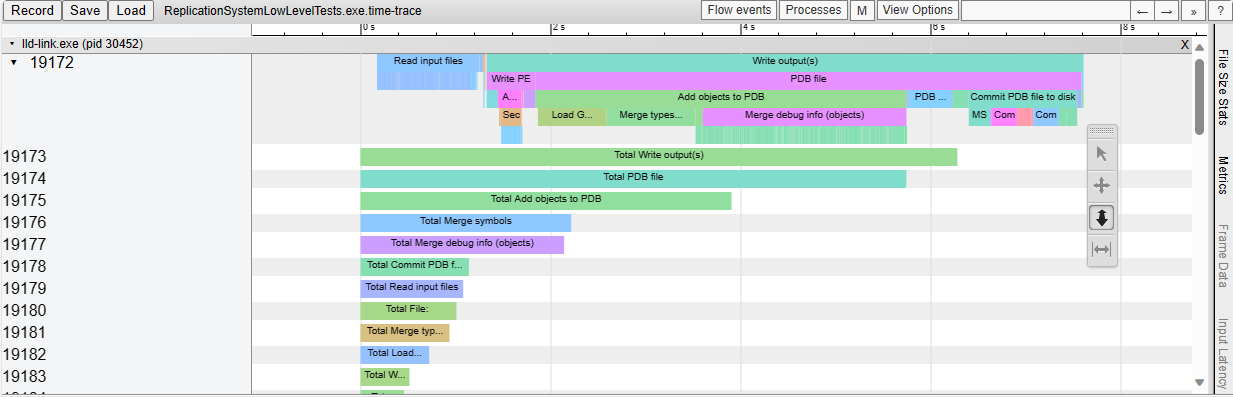
This adds support for generating Chrome-tracing .json profile traces in
the LLD COFF driver.
Also add the necessary time scopes, so that the profile trace shows in
great detail which tasks are executed.
As an example, this is what we see when linking a Unreal Engine
executable:
Close#57618: currently we align the end of PT_GNU_RELRO to a
common-page-size
boundary, but do not align the end of the associated PT_LOAD. This is
benign
when runtime_page_size >= common-page-size.
However, when runtime_page_size < common-page-size, it is possible that
`alignUp(end(PT_LOAD), page_size) < alignDown(end(PT_GNU_RELRO),
page_size)`.
In this case, rtld's mprotect call for PT_GNU_RELRO will apply to
unmapped
regions and lead to an error, e.g.
```
error while loading shared libraries: cannot apply additional memory protection after relocation: Cannot allocate memory
```
To fix the issue, add a padding section .relro_padding like mold, which
is contained in the PT_GNU_RELRO segment and the associated PT_LOAD
segment. The section also prevents strip from corrupting PT_LOAD program
headers.
.relro_padding has the largest `sortRank` among RELRO sections.
Therefore, it is naturally placed at the end of `PT_GNU_RELRO` segment
in the absence of `PHDRS`/`SECTIONS` commands.
In the presence of `SECTIONS` commands, we place .relro_padding
immediately before a symbol assignment using DATA_SEGMENT_RELRO_END (see
also https://reviews.llvm.org/D124656), if present.
DATA_SEGMENT_RELRO_END is changed to align to max-page-size instead of
common-page-size.
Some edge cases worth mentioning:
* ppc64-toc-addis-nop.s: when PHDRS is present, do not append
.relro_padding
* avoid-empty-program-headers.s: when the only RELRO section is .tbss,
it is not part of PT_LOAD segment, therefore we do not append
.relro_padding.
---
Close#65002: GNU ld from 2.39 onwards aligns the end of PT_GNU_RELRO to
a
max-page-size boundary (https://sourceware.org/PR28824) so that the last
page is
protected even if runtime_page_size > common-page-size.
In my opinion, losing protection for the last page when the runtime page
size is
larger than common-page-size is not really an issue. Double mapping a
page of up
to max-common-page for the protection could cause undesired VM waste.
Internally
we had users complaining about 2MiB max-page-size applying to shared
objects.
Therefore, the end of .relro_padding is padded to a common-page-size
boundary. Users who are really anxious can set common-page-size to match
their runtime page size.
---
17 tests need updating as there are lots of change detectors.
This patch adds support to lld for --fat-lto-objects. We add a new
--fat-lto-objects option to LLD, and slightly change how it chooses input
files in the driver when the option is set.
Fat LTO objects contain both LTO compatible IR, as well as generated object
code. This allows users to defer the choice of whether to use LTO or not to
link-time. This is a feature available in GCC for some time, and makes the
existing -ffat-lto-objects option functional in the same way as GCC's.
If the --fat-lto-objects option is passed to LLD and the input files are fat
object files, then the linker will chose the LTO compatible bitcode sections
embedded within the fat object and link them together using LTO. Otherwise,
standard object file linking is done using the assembly section in the object
files.
The previous version of this patch had a missing `REQUIRES: x86` line in
`fatlto.invalid.s`. Additionally, it was reported that this patch caused
a test failure in `export-dynamic-symbols.s`, however,
29112a9946 disabled the
`export-dynamic-symbols.s` test on Windows due to a quotation difference
between platforms, unrelated to this patch.
Original RFC: https://discourse.llvm.org/t/rfc-ffat-lto-objects-support/63977
Reviewed By: MaskRay
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D146778
This adds support for the LoongArch ELF psABI v2.00 [1] relocation
model to LLD. The deprecated stack-machine-based psABI v1 relocs are not
supported.
The code is tested by successfully bootstrapping a Gentoo/LoongArch
stage3, complete with common GNU userland tools and both the LLVM and
GNU toolchains (GNU toolchain is present only for building glibc,
LLVM+Clang+LLD are used for the rest). Large programs like QEMU are
tested to work as well.
[1]: https://loongson.github.io/LoongArch-Documentation/LoongArch-ELF-ABI-EN.html
Reviewed By: MaskRay, SixWeining
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D138135
This reverts commit c9953d9891 and a
forward fix in 3a45b843de.
D14677 causes some failure on windows bots that the forward fix did not
address. Thus I'm reverting until the underlying cause can me triaged.
This patch adds support to lld for --fat-lto-objects. We add a new
--fat-lto-objects flag to LLD, and slightly change how it chooses input
files in the driver when the flag is set.
Fat LTO objects contain both LTO compatible IR, as well as generated object
code. This allows users to defer the choice of whether to use LTO or not to
link-time. This is a feature available in GCC for some time, and makes the
existing -ffat-lto-objects flag functional in the same way as GCC's.
If the --fat-lto-objects option is passed to LLD and the input files are fat
object files, then the linker will chose the LTO compatible bitcode sections
embedded within the fat object and link them together using LTO. Otherwise,
standard object file linking is done using the assembly section in the object
files.
Original RFC: https://discourse.llvm.org/t/rfc-ffat-lto-objects-support/63977
Depends on D146777
Reviewed By: MaskRay
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D146778
We want lld-link to automatically find compiler-rt's and
libc++ when it's in the same directory as the rest of the
toolchain. This is because on Windows linking isn't done
via the clang driver - but instead invoked directly.
This prepends: <llvm>/lib <llvm>/lib/clang/XX/lib and
<llvm>/lib/clang/XX/lib/windows automatically to the library
search paths.
Related to #63827
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D151188
This patch is spun out of https://reviews.llvm.org/D151188
and makes it possible for lld-link to find libraries with
relative paths. This will be used later to implement the
changes to autolinking runtimes explained in #63827
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D155268
--remap-inputs-file= can be specified multiple times, each naming a
remap file that contains `from-glob=to-file` lines or `#`-led comments.
('=' is used a separator a la -fdebug-prefix-map=)
--remap-inputs-file= can be used to:
* replace an input file. E.g. `"*/libz.so=exp/libz.so"` can replace a resolved
`-lz` without updating the input file list or (if used) a response file.
When debugging an application where a bug is isolated to one single
input file, this option gives a convenient way to test fixes.
* remove an input file with `/dev/null` (changed to `NUL` on Windows), e.g.
`"a.o=/dev/null"`. A build system may add unneeded dependencies.
This option gives a convenient way to test the result removing some inputs.
`--remap-inputs=a.o=aa.o` can be specified to provide one pattern without using
an extra file.
(bash/zsh process substitution is handy for specifying a pattern without using
a remap file, e.g. `--remap-inputs-file=<(printf 'a.o=aa.o')`, but it may be
unavailable in some systems. An extra file can be inconvenient for a build
system.)
Exact patterns are tested before wildcard patterns. In case of a tie, the first
patterns wins. This is an implementation detail that users should not rely on.
Co-authored-by: Marco Elver <elver@google.com>
Link: https://discourse.llvm.org/t/rfc-support-exclude-inputs/70070
Reviewed By: melver, peter.smith
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D148859
Embedded systems that do not use an ELF loader locate the
.ARM.exidx exception table via linker defined __exidx_start and
__exidx_end rather than use the PT_ARM_EXIDX program header. This
means that some linker scripts such as the picolibc C library's
linker script, do not have the .ARM.exidx sections at offset 0 in
the OutputSection. For example:
.except_unordered : {
. = ALIGN(8);
PROVIDE(__exidx_start = .);
*(.ARM.exidx*)
PROVIDE(__exidx_end = .);
} >flash AT>flash :text
This is within the specification of Arm exception tables, and is
handled correctly by ld.bfd.
This patch has 2 parts. The first updates the writing of the data
of the .ARM.exidx SyntheticSection to account for a non-zero
OutputSection offset. The second part makes the PT_ARM_EXIDX program
header generation a special case so that it covers only the
SyntheticSection and not the parent OutputSection. While not strictly
necessary for programs locating the exception tables via the symbols
it may cause ELF utilities that locate the exception tables via
the PT_ARM_EXIDX program header to fail. This does not seem to be the
case for GNU and LLVM readelf which seems to look for the
SHT_ARM_EXIDX section.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D148033
Currently we take the first SHT_RISCV_ATTRIBUTES (.riscv.attributes) as the
output. If we link an object without an extension with an object with the
extension, the output Tag_RISCV_arch may not contain the extension and some
tools like objdump -d will not decode the related instructions.
This patch implements
Tag_RISCV_stack_align/Tag_RISCV_arch/Tag_RISCV_unaligned_access merge as
specified by
https://github.com/riscv-non-isa/riscv-elf-psabi-doc/blob/master/riscv-elf.adoc#attributes
For the deprecated Tag_RISCV_priv_spec{,_minor,_revision}, dump the attribute to
the output iff all input agree on the value. This is different from GNU ld but
our simple approach should be ok for deprecated tags.
`RISCVAttributeParser::handler` currently warns about unknown tags. This
behavior is retained. In GNU ld arm, tags >= 64 (mod 128) are ignored with a
warning. If RISC-V ever wants to do something similar
(https://github.com/riscv-non-isa/riscv-elf-psabi-doc/issues/352), consider
documenting it in the psABI and changing RISCVAttributeParser.
Like GNU ld, zero value integer attributes and empty string attributes are not
dumped to the output.
Reviewed By: asb, kito-cheng
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D138550
Allowing incorrect version scripts is not a helpful default. Flip that
to help users find their bugs at build time rather than at run time.
Reviewed By: MaskRay
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D135402
https://github.com/riscv/riscv-elf-psabi-doc/pull/190 introduced STO_RISCV_VARIANT_CC.
The linker should:
* Copy the STO_RISCV_VARIANT_CC bit to .symtab/.dynsym: already fulfilled after
82ed93ea05
* Produce DT_RISCV_VARIANT_CC if at least one R_RISCV_JUMP_SLOT relocation
references a symbol with the STO_RISCV_VARIANT_CC bit. Done by this patch.
Reviewed By: kito-cheng
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D107951
Solve two issues that showed up when using LLD with Unreal Engine & FASTBuild:
1. It seems the S_OBJNAME record doesn't always record the "precomp signature". We were relying on that to match the PCH.OBJ with their dependent-OBJ.
2. MSVC link.exe is able to link a PCH.OBJ when the "precomp signatureÈ doesn't match, but LLD was failing. This was occuring since the Unreal Engine Build Tool was compiling the PCH.OBJ, but the dependent-OBJ were compiled & cached through FASTBuild. Upon a clean rebuild, the PCH.OBJs were recompiled by the Unreal Build Tool, thus the "precomp signatures" were changing; however the OBJs were already cached by FASTBuild, thus having an old "precomp signatures".
We now ignore "precomp signatures" and properly fallback to cmd-line name lookup, like MSVC link.exe does, and only fail if the PCH.OBJ type stream doesn't match the count expected by the dependent-OBJ.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D136762
Previously, we used SHA-1 for hashing the CodeView type records.
SHA-1 in `GloballyHashedType::hashType()` is coming top in the profiles. By simply replacing with BLAKE3, the link time is reduced in our case from 15 sec to 13 sec. I am only using MSVC .OBJs in this case. As a reference, the resulting .PDB is approx 2.1GiB and .EXE is approx 250MiB.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D137101
MSVC records the command line arguments in S_ENVBLOCK, skipping the input file arguments.
This patch adds this filtering on lld-link side.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D137723
Allowing incorrect version scripts is not a helpful default. Flip that
to help users find their bugs at build time rather than at run time.
Reviewed By: MaskRay
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D135402
Mach-O ld64 supports -w to suppress warnings. GNU ld 2.40 will support the
option as well (https://sourceware.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=29654).
This feature has some small value. E.g. when analyzing a large executable with
relocation overflow issues, we may use --noinhibit-exec --emit-relocs to get an
output file with static relocations despite relocation overflow issues. -w can
significantly improve the link time as printing the massive warnings is slow.
Reviewed By: peter.smith
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D136569
This reverts commit 096f93e73d.
Revert "[Libomptarget] Make the plugins ingore undefined exported symbols"
This reverts commit 3f62314c23.
Revert "[LLD] Enable --no-undefined-version by default."
This reverts commit 7ec8b0d162.
Three commits are reverted because of the current omp build fail
with GNU ld. See discussion here: https://reviews.llvm.org/rG096f93e73dc3
Allowing incorrect version scripts is not a helpful default. Flip that
to help users find their bugs at build time rather than at run time.
Reviewed By: MaskRay
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D135402
`clang -gz=zstd a.o` passes this option to the linker. This option compresses output
debug sections with zstd and sets ch_type to ELFCOMPRESS_ZSTD. As of today, very
few DWARF consumers recognize ELFCOMPRESS_ZSTD.
Use the llvm::zstd::compress API with level llvm::zstd::DefaultCompression (5),
which we may tune after we have more experience with zstd output.
zstd has built-in parallel compression support (so we don't need to do D117853
for zlib), which is not leveraged yet.
Reviewed By: peter.smith
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D133548
so that lld accepts relocatable object files produced by `clang -c -g -gz=zstd`.
We don't want to increase the size of InputSection, so do redundant but cheap
ch_type checks instead.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D129406
These will be LLD-specific options to support Control Flow Guard for the
MinGW target. They are disabled by default, but enabling `--guard-cf`
will also enable `--guard-longjmp` unless `--no-guard-longjmp` is also
specified. These options maps to `-guard:cf,[no]longjmp`.
Note that these features require the `_load_config_used` symbol to
contain the load config directory and be filled with the required
symbols. While current versions of mingw-w64 do not supply this symbol,
the user can provide their own version of it.
Reviewed By: MaskRay, rnk
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D132808
This is an entirely new embedded directive - extending the GNU ld
command line option --exclude-symbols to be usable in embedded
directives too.
(GNU ld.bfd also got support for the same new directive, currently in
the latest git version, after the 2.39 branch.)
This works as an inverse to the regular embedded dllexport directives,
for cases when autoexport of all eligible symbols is performed.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D130120
This adds support for the existing GNU ld command line option, which
allows excluding individual symbols from autoexport (when linking a
DLL and no symbols are marked explicitly as dllexported).
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D130118
This was recently introduced in GNU linkers and it makes sense for
ld.lld to have the same support. This implementation omits checking if
the input string is valid json to reduce size bloat.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D131439
This just removes the code that gates the logic. The main issue here is
perf impact: without {D122258}, LLD takes a significant perf hit because
it now has to do a lot more work in the input parsing phase. But with
that change to eliminate unnecessary EH frames from input object files,
the perf overhead here is minimal. Concretely, here are the numbers for
some builds as measured on my 16-core Mac Pro:
**chromium_framework**
This is without the use of `-femit-dwarf-unwind=no-compact-unwind`:
base diff difference (95% CI)
sys_time 1.826 ± 0.019 1.962 ± 0.034 [ +6.5% .. +8.4%]
user_time 9.306 ± 0.054 9.926 ± 0.082 [ +6.2% .. +7.1%]
wall_time 8.225 ± 0.068 8.947 ± 0.128 [ +8.0% .. +9.6%]
samples 15 22
With that flag enabled, the regression mostly disappears, as hoped:
base diff difference (95% CI)
sys_time 1.839 ± 0.062 1.866 ± 0.068 [ -0.9% .. +3.8%]
user_time 9.452 ± 0.068 9.490 ± 0.067 [ -0.1% .. +0.9%]
wall_time 8.383 ± 0.127 8.452 ± 0.114 [ -0.1% .. +1.8%]
samples 17 21
**Unnamed internal app**
Without `-femit-dwarf-unwind`, this is the perf hit:
base diff difference (95% CI)
sys_time 1.372 ± 0.029 1.317 ± 0.024 [ -4.6% .. -3.5%]
user_time 2.835 ± 0.028 2.980 ± 0.027 [ +4.8% .. +5.4%]
wall_time 3.205 ± 0.079 3.383 ± 0.066 [ +4.9% .. +6.2%]
samples 102 83
With `-femit-dwarf-unwind`, the perf hit almost disappears:
base diff difference (95% CI)
sys_time 1.274 ± 0.026 1.270 ± 0.025 [ -0.9% .. +0.3%]
user_time 2.812 ± 0.023 2.822 ± 0.035 [ +0.1% .. +0.7%]
wall_time 3.166 ± 0.047 3.174 ± 0.059 [ -0.2% .. +0.7%]
samples 95 97
Just for fun, I measured the impact of `-femit-dwarf-unwind` on ld64
(`base` has the extra DWARF unwind info in the input object files,
`diff` doesn't):
base diff difference (95% CI)
sys_time 1.128 ± 0.010 1.124 ± 0.023 [ -1.3% .. +0.6%]
user_time 7.176 ± 0.030 7.106 ± 0.094 [ -1.5% .. -0.4%]
wall_time 7.874 ± 0.041 7.795 ± 0.121 [ -1.7% .. -0.3%]
samples 16 25
And for LLD:
base diff difference (95% CI)
sys_time 1.315 ± 0.019 1.280 ± 0.019 [ -3.2% .. -2.0%]
user_time 2.980 ± 0.022 2.822 ± 0.016 [ -5.5% .. -5.0%]
wall_time 3.369 ± 0.038 3.175 ± 0.033 [ -6.2% .. -5.3%]
samples 47 47
So parsing the extra EH frames is a lot more expensive for us than for
ld64. But given that we are quite a lot faster than ld64 to begin with,
I guess this isn't entirely unexpected...
Reviewed By: #lld-macho, oontvoo
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D129540
Add FORCE_LLD_DIAGNOSTICS_CRASH inspired by the existing
FORCE_CLANG_DIAGNOSTICS_CRASH.
This is particularly useful for people customizing LLD as they may
want to modify the crash reporting behavior.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D128195
`--time-trace=foo` has the same behavior as `--time-trace --time-trace-file=<file>`
had previously.
Also, for mac, make --time-trace-granularity *not* imply --time-trace, to match
behavior of the ELF port.
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D128451
.zdebug is unlikely used any longer: gcc -gz switched from legacy
.zdebug to SHF_COMPRESSED with binutils 2.26 (2016), which has been
several years. clang 14 dropped -gz=zlib-gnu support. According to
Debian Code Search (`gz=zlib-gnu`), no project uses -gz=zlib-gnu.
Remove .zdebug support to (a) simplify code and (b) allow removal of llvm-mc's
--compress-debug-sections=zlib-gnu.
In case the old object file `a.o` uses .zdebug, run `objcopy --decompress-debug-sections a.o`
Reviewed By: peter.smith
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D126793
We picked common-page-size to match GNU ld. Recently, the resolution to GNU ld
https://sourceware.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=28824 (milestone: 2.39) switched
to max-page-size so that the last page can be protected by RELRO in case the
system page size is larger than common-page-size.
Thanks to our two RW PT_LOAD scheme (D58892), switching to max-page-size does
not change file size (while GNU ld's scheme may increase file size).
Reviewed By: peter.smith
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D125410
D86142 introduced --fortran-common and defaulted it to true (matching GNU ld
but deviates from gold/macOS ld64). The default state was motivated by transparently
supporting some FORTRAN 77 programs (Fortran 90 deprecated common blocks).
Now I think it again. I believe we made a mistake to change the default:
* this is a weird and legacy rule, though the breakage is very small
* --fortran-common introduced complexity to parallel symbol resolution and will slow down it
* --fortran-common more likely causes issues when users mix COMMON and
STB_GLOBAL definitions (see https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/issues/48570 and
https://maskray.me/blog/2022-02-06-all-about-common-symbols).
I have seen several issues in our internal projects and Android.
On the other hand, --no-fortran-common is safer since
COMMON/STB_GLOBAL have the same semantics related to archive member extraction.
Therefore I think we should switch back, not punishing the common uage.
A platform wanting --fortran-common can implement ld.lld as a shell script
wrapper around `lld -flavor gnu --fortran-common "$@"`.
Reviewed By: ikudrin, sfertile
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D122450
https://discourse.llvm.org/t/parallel-input-file-parsing/60164
initializeSymbols currently sets Defined::section and handles non-prevailing
COMDAT groups. Move the code to the parallel postParse to reduce work from the
single-threading code path and make parallel section initialization infeasible.
Postpone reporting duplicate symbol errors so that the messages have the
section information. (`Defined::section` is assigned in postParse and another
thread may not have the information).
* duplicated-synthetic-sym.s: BinaryFile duplicate definition (very rare) now
has no section information
* comdat-binding: `%t/w.o %t/g.o` leads to an undesired undefined symbol. This
is not ideal but we report a diagnostic to inform that this is unsupported.
(See release note)
* comdat-discarded-lazy.s: %tdef.o is unextracted. The new behavior (discarded
section error) makes more sense
* i386-comdat.s: switched to a better approach working around
.gnu.linkonce.t.__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx in glibc<2.32 for x86-32.
Drop the ancient no-longer-relevant workaround for __i686.get_pc_thunk.bx
Depends on D120640
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D120626
https://discourse.llvm.org/t/parallel-input-file-parsing/60164
initializeSymbols currently sets Defined::section and handles non-prevailing
COMDAT groups. Move the code to the parallel postParse to reduce work from the
single-threading code path and make parallel section initialization infeasible.
Postpone reporting duplicate symbol errors so that the messages have the
section information. (`Defined::section` is assigned in postParse and another
thread may not have the information).
* duplicated-synthetic-sym.s: BinaryFile duplicate definition (very rare) now
has no section information
* comdat-binding: `%t/w.o %t/g.o` leads to an undesired undefined symbol. This
is not ideal but we report a diagnostic to inform that this is unsupported.
(See release note)
* comdat-discarded-lazy.s: %tdef.o is unextracted. The new behavior (discarded
section error) makes more sense
Depends on D120640
Reviewed By: peter.smith
Differential Revision: https://reviews.llvm.org/D120626